
Water treatment solutions
Discover our water treatment systems designed to many professional sectors
Discover our water treatment processes by ultraviolets, Ozone, AOP and Salt electrolysis:
1. Ultraviolet light (UV): an effective method to eradicate micro-organisms
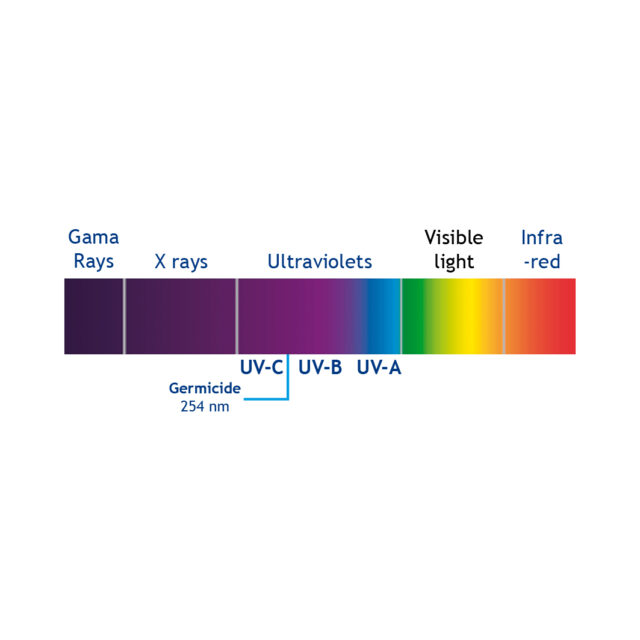
The sun emits light invisible to the human eye (ultraviolet light) that is largely absorbed by the earth’s ozone layer. The singularity of UV light is its range of wavelengths between 200 and 300 nanometers (UV-C) which are germicidal, that is, they have the ability to deactivate microorganisms such as viruses, bacteria, algae, molds… including Legionella, Cryptosporidium, Giardia and Toxoplasmas.
The efficient dose of UV to fight micro-organisms
The UV dose is the UV-C energy that must be absorbed by living microorganisms to be inactivated. This table shows the UV-C dose level needed (expressed in millijoules (mJ) /cm²) to inactivate 99.9% of microorganisms:
| MICRO-ORGANISM | UV-C DOSES |
| BACTERIA Staphylococcus E.Coli Legionnella Pneumophila Salmonella enteridis Streptococcus Faecali | 8,5 mJ/cm2 10,5 mJ/cm2 6,9 mJ/cm2 9 mJ/cm2 10 mJ/cm2 |
| ALGAE Chlorella vulgaris | 22 mJ/cm2 |
| PROTOZOARS Cryptosporidium | 16 mJ/cm2 |
| VIRUS Hepatitis SARS-CoV-2 | 8 mJ/cm2 12 mJ/cm2 |
| MOULD Aspergillus Niger | 330 mJ/cm2 |
2. The Ozone water disinfection process
(O3) is extensively used in the industry for water treatment, pathogen control, and oxidation of contaminants. It’s a highly active form of oxygen (O₂), more effective than many commercially available chemical treatments for both disinfection and water quality improvement. It has the unique property of breaking down naturally and safely into its original oxygen form. Ozone is also able to improve the efficiency of up and downstream technologies, contributing to water reuse and energy saving potential in the wider water treatment system.
As nature’s most powerful oxidant, ozone is a simple and effective way to break down contaminants in a number applications.
3. Water treatment by AOP

The triogen® AOP (advanced oxidation process) technology is a specific water treatment process that results from a combination of Ozone and ultraviolet radiation that will form highly reactive hydroxyl free radicals. These hydroxyl radicals will eliminate all organic pollutants and allow a perfect control of pathogenic species thanks to the inactivation of chlorine-resistant microorganisms.
The UV light destroys by photochemistry the residual Ozone in the water, thus avoiding the need for deozonation equipment.
4. Salt electrolysis

The salt water chlorinator is an automated chemical chlorine treatment method that works on the perpetual cycle model. The electrolysis converts the salt in the pool into chlorine without the addition of chemicals. From this very slightly salty water, an electrolysis cell produces chlorine and diffuses it into the water to eliminate bacteria and algae, without residue or pollution.
